Understanding Diabetes And Blood Sugar Levels
Overview Of Diabetes And Its Impact On Blood Sugar Levels
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or is unable to properly use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells and be used for energy. When insulin is not functioning properly, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is often caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors and is characterized by insulin resistance. In both types of diabetes, blood sugar levels can become dangerously high if not properly managed.
Factors To Consider When Assessing The Impact Of Orange Juice On Blood Sugar
When assessing the impact of orange juice on blood sugar levels, several factors should be considered:
- Carbohydrate content: Orange juice contains natural sugars, which can raise blood sugar levels. One cup of orange juice typically contains around 26 grams of carbohydrates.
- Glycemic index: The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI, such as sugary drinks like orange juice, can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels.
- Portion size: The amount of orange juice consumed can also impact blood sugar levels. Drinking a small glass of orange juice is likely to have a different effect than drinking a larger serving.
- Timing: The timing of consuming orange juice can also play a role in its impact on blood sugar levels. Consuming it with a meal or incorporating it into a balanced diet can help mitigate spikes in blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, understanding diabetes and its impact on blood sugar levels is crucial for managing the condition effectively. Factors such as the carbohydrate content, glycemic index, portion size, and timing of orange juice consumption should be considered when assessing its impact on blood sugar levels. Discussing individual dietary needs with a healthcare professional can help determine the appropriate consumption of orange juice for individuals with diabetes.
Nutritional Profile Of Orange Juice
Macronutrients And Micronutrients Found In Orange Juice
Orange juice is a popular beverage that is known for its high vitamin C content. However, it also contains other macronutrients and micronutrients that can impact blood sugar levels. Here is a breakdown of the key nutrients found in orange juice:
- Carbohydrates: Orange juice contains natural sugars, which are a type of carbohydrate. One cup of orange juice typically contains around 26 grams of carbohydrates.
- Fiber: While orange juice is not a significant source of dietary fiber, it does contain some. One cup of orange juice provides about 0.5 grams of fiber.
- Vitamin C: Orange juice is well-known for its high vitamin C content. One cup of orange juice can provide over 100% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C.
- Potassium: Orange juice is a good source of potassium, an essential mineral that plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels. One cup of orange juice can provide about 10% of the daily recommended intake of potassium.
- Folate: Orange juice is also a source of folate, a B-vitamin that is important for overall health. One cup of orange juice typically contains around 10% of the daily recommended intake of folate.
Impact Of These Nutrients On Blood Sugar Levels
The nutrients found in orange juice can have different effects on blood sugar levels. Here are some key points to consider:
- Carbohydrates: The natural sugars found in orange juice can raise blood sugar levels. It is important to consider the amount of carbohydrates consumed when managing blood sugar levels.
- Fiber: While orange juice does contain some fiber, it is not enough to have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. However, consuming whole fruits that contain more fiber, like oranges themselves, may have a different effect on blood sugar levels.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C does not directly impact blood sugar levels. However, it is an important antioxidant that plays a role in overall health and may have indirect benefits for individuals with diabetes.
- Potassium: Potassium is important for regulating blood sugar levels and may help improve insulin sensitivity. Consuming orange juice can contribute to overall potassium intake, which can have a positive impact on blood sugar control.
- Folate: Folate is important for overall health but does not directly impact blood sugar levels.
Understanding the macronutrients and micronutrients found in orange juice can help individuals with diabetes make informed choices about their diet. It is important to consider the overall balance of nutrients and to discuss individual dietary needs with a healthcare professional.

Glycemic Index Of Orange Juice
Explanation Of Glycemic Index And Its Relevance To Blood Sugar Control
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels after it is consumed. Foods with a high GI are quickly digested and cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, while foods with a low GI are digested more slowly and have a slower, more gradual impact on blood sugar levels. Understanding the glycemic index of foods can be helpful for individuals with diabetes in managing their blood sugar levels.
Glycemic Index Of Orange Juice And Its Effects On Blood Sugar Levels
The glycemic index of orange juice varies depending on factors such as the ripeness of the oranges and the processing methods used. Freshly squeezed orange juice typically has a higher glycemic index compared to whole oranges, as the juicing process breaks down the fiber and releases the natural sugars more quickly.
On average, orange juice has a medium to high glycemic index, with values ranging from around 52 to 80. This means that it can cause a moderate to rapid increase in blood sugar levels after consumption.
For individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels, it is important to consume orange juice in moderation and consider the overall balance of nutrients in their diet. Pairing orange juice with a source of protein or fiber, such as having it with a meal or snack that includes eggs or whole grains, can help slow down the absorption of sugars and minimize the impact on blood sugar levels.
Talking to a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on incorporating orange juice into a balanced diet for individuals with diabetes.
Effect Of Natural Sugars In Orange Juice
Breakdown Of Natural Sugars In Orange Juice And Their Impact On Blood Sugar
Orange juice contains natural sugars, primarily fructose. These sugars are released quickly into the bloodstream when orange juice is consumed, leading to an increase in blood sugar levels. While natural sugars are generally considered healthier than added sugars, they can still have an impact on blood sugar control.
The glycemic index (GI) of orange juice varies depending on factors such as the ripeness of the oranges and the processing methods used. Freshly squeezed orange juice typically has a higher GI compared to whole oranges, as the juicing process breaks down the fiber and releases the natural sugars more quickly.
On average, orange juice has a medium to high glycemic index, with values ranging from around 52 to 80. This means that it can cause a moderate to rapid increase in blood sugar levels after consumption.
Comparing The Effects Of Natural Sugars In Orange Juice To Added Sugars
While natural sugars in orange juice can impact blood sugar levels, they are generally considered healthier than added sugars. Added sugars, such as those found in processed foods and sugary beverages, have a higher glycemic index and can cause a more rapid and significant increase in blood sugar levels.
It is important to note that consuming excessive amounts of any sugar, whether natural or added, can lead to negative health effects, including weight gain and an increased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
When consuming orange juice or any other food or beverage high in natural sugars, it is important to do so in moderation and consider the overall balance of nutrients in the diet. Pairing orange juice with a source of protein or fiber, such as having it with a meal or snack that includes eggs or whole grains, can help slow down the absorption of sugars and minimize the impact on blood sugar levels.
Talking to a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on incorporating orange juice into a balanced diet for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Effect Of Natural Sugars In Orange Juice
Breakdown Of Natural Sugars In Orange Juice And Their Impact On Blood Sugar
Orange juice contains natural sugars, primarily fructose. These sugars are released quickly into the bloodstream when orange juice is consumed, leading to an increase in blood sugar levels. While natural sugars are generally considered healthier than added sugars, they can still have an impact on blood sugar control.
The glycemic index (GI) of orange juice varies depending on factors such as the ripeness of the oranges and the processing methods used. Freshly squeezed orange juice typically has a higher GI compared to whole oranges, as the juicing process breaks down the fiber and releases the natural sugars more quickly.
On average, orange juice has a medium to high glycemic index, with values ranging from around 52 to 80. This means that it can cause a moderate to rapid increase in blood sugar levels after consumption.
Comparing The Effects Of Natural Sugars In Orange Juice To Added Sugars
While natural sugars in orange juice can impact blood sugar levels, they are generally considered healthier than added sugars. Added sugars, such as those found in processed foods and sugary beverages, have a higher glycemic index and can cause a more rapid and significant increase in blood sugar levels.
It is important to note that consuming excessive amounts of any sugar, whether natural or added, can lead to negative health effects, including weight gain and an increased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
When consuming orange juice or any other food or beverage high in natural sugars, it is important to do so in moderation and consider the overall balance of nutrients in the diet. Pairing orange juice with a source of protein or fiber, such as having it with a meal or snack that includes eggs or whole grains, can help slow down the absorption of sugars and minimize the impact on blood sugar levels.
Talking to a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on incorporating orange juice into a balanced diet for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Fiber Content In Orange Juice
Role Of Fiber In Blood Sugar Regulation
Fiber plays an important role in blood sugar regulation. It slows down the digestion and absorption of sugars, resulting in a slower and more controlled release of glucose into the bloodstream. This can help prevent sharp spikes in blood sugar levels and promote better blood sugar control.
Analyzing The Fiber Content In Orange Juice And Its Effects On Blood Sugar Levels
While oranges are a good source of dietary fiber, the juicing process removes most of the fiber from orange juice. This means that orange juice has a significantly lower fiber content compared to whole oranges.
The lack of fiber in orange juice can result in a faster release of natural sugars into the bloodstream, leading to a quicker spike in blood sugar levels. This is why consuming whole oranges is generally considered to be a better option for blood sugar control compared to drinking orange juice.
It is worth noting that some commercially available orange juices may contain added fiber to compensate for the loss during juicing. These fortified orange juices can provide a higher fiber content compared to regular orange juice.
In conclusion, while orange juice can contribute to an increase in blood sugar levels due to its natural sugar content, it is generally considered healthier than beverages with added sugars. However, individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels should consume orange juice in moderation and consider other options, such as whole oranges or fortified orange juices, to incorporate more fiber into their diet. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on the appropriate consumption of orange juice for blood sugar control.
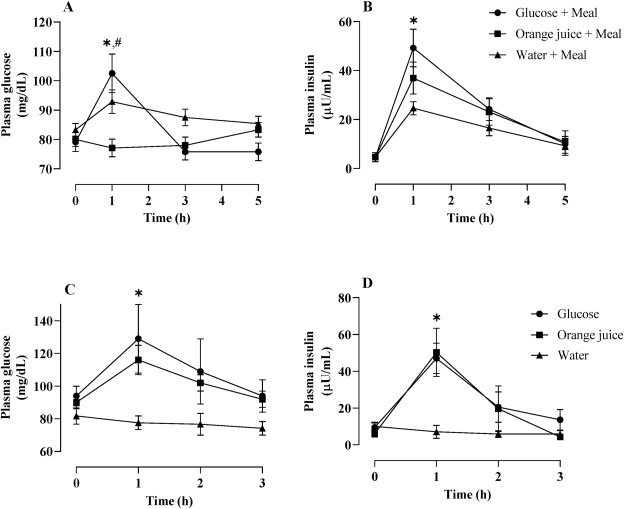
Influence Of Portion Size And Timing
Impact Of Portion Size On Blood Sugar Levels
Consuming larger portions of orange juice can result in a more significant increase in blood sugar levels compared to smaller portions. This is because a larger portion contains a higher amount of natural sugars, which are quickly absorbed into the bloodstream. It is important for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels to be mindful of portion sizes when consuming orange juice.
The Importance Of Timing When Consuming Orange Juice For Diabetics
The timing of consuming orange juice can also impact blood sugar levels, particularly for individuals with diabetes. Drinking orange juice on an empty stomach or without pairing it with other foods can lead to a faster absorption of sugars and a more rapid increase in blood sugar levels. It is recommended for diabetics to consume orange juice alongside a balanced meal or snack that includes sources of protein or fiber. This can help slow down the absorption of sugars and prevent sharp spikes in blood sugar levels.
In summary, the portion size and timing of consuming orange juice can have significant effects on blood sugar levels, particularly for individuals with diabetes. Consuming smaller portions and pairing orange juice with protein or fiber-rich foods can help regulate the release of sugars into the bloodstream and maintain better blood sugar control. Individuals should consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice on portion sizes and timing when incorporating orange juice into their diet for blood sugar management.
Benefits Of Freshly Squeezed Orange Juice
Potential Benefits Of Freshly Squeezed Orange Juice For Diabetics
Freshly squeezed orange juice can offer several potential benefits for individuals with diabetes, including:
- Rich in nutrients: Orange juice is a good source of essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, potassium, and folate. These nutrients play a vital role in maintaining overall health and supporting various bodily functions.
- Natural sugars: While orange juice does contain natural sugars, it doesn’t have added sugars like many store-bought versions. This can be advantageous for diabetics who need to monitor their sugar intake more closely.
- Fiber content: Freshly squeezed orange juice contains dietary fiber that helps slow down the absorption of sugars into the bloodstream. This can help prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Antioxidants: Oranges are packed with antioxidants, including flavonoids and vitamin C, which can help reduce inflammation and protect against oxidative damage.
Factors To Consider When Choosing Between Store-bought And Fresh Orange Juice
When deciding between store-bought and freshly squeezed orange juice, it’s important to consider the following factors:
| Factors | Store-Bought Orange Juice | Freshly Squeezed Orange Juice |
|---|---|---|
| Taste | May have artificial flavors or preservatives | Natural, pure taste |
| Nutrient Content | May contain added sugars and have lower nutrient levels | Higher nutrient levels with no added sugars |
| Fiber | Typically low fiber content | Contains fiber, helping to slow down sugar absorption |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Can be more expensive, especially when freshly squeezed from organic oranges |
In conclusion, freshly squeezed orange juice can provide several potential benefits for individuals with diabetes. It has a higher nutrient content, natural sugars, and fiber compared to store-bought versions. However, factors such as taste, nutrient content, fiber, and cost should be considered when deciding between store-bought and freshly squeezed orange juice. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can help individuals make an informed decision based on their individual needs and preferences.
Recommendations For Incorporating Orange Juice Into A Diabetic Diet
Guidelines For Safely Consuming Orange Juice As A Diabetic
- It is important for individuals with diabetes to monitor their carbohydrate intake, as carbohydrates have a direct impact on blood sugar levels. When incorporating orange juice into a diabetic diet, it is recommended to consider the following guidelines:
- Portion control: Limit the amount of orange juice consumed in one serving to avoid excessive intake of natural sugars.
- Timing: Consume orange juice as part of a balanced meal or snack that includes protein and healthy fats. This can help slow down the absorption of sugars into the bloodstream and prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Testing blood sugar levels: Regularly monitor blood sugar levels before and after consuming orange juice to understand its impact on individual glycemic responses. This can help determine the appropriate portion size and frequency of consumption.
- Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian: Seek guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to personalize dietary recommendations and ensure proper diabetes management.
Tips For Balancing Orange Juice Intake With Other Dietary Considerations
- While orange juice can be enjoyed as part of a diabetic diet, it is important to consider other dietary factors to maintain overall health:
- Variety of fruits and vegetables: Incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables into the diet to ensure a balanced intake of nutrients and antioxidants.
- Whole fruits: Instead of solely relying on orange juice for vitamin C and other nutrients, consider consuming whole oranges or other fruits to benefit from their fiber content and slower sugar absorption.
- Hydration: Remember to hydrate adequately by drinking water throughout the day, in addition to consuming orange juice.
- Individualized meal planning: Work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan that considers individual dietary needs, preferences, and overall diabetes management goals.
- Physical activity: Engage in regular physical activity to help manage blood sugar levels and overall health.
Incorporating orange juice into a diabetic diet can provide various benefits, but it is essential to consider portion sizes, timing of consumption, and overall dietary balance. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended for personalized recommendations and to ensure the safest and most effective inclusion of orange juice in a diabetic diet.
Conclusion
Summary Of The Impact Of Orange Juice On Blood Sugar Levels
- Portion control and timing are crucial when consuming orange juice as a diabetic.- Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels before and after consuming orange juice can help determine appropriate portion sizes and frequency.- Consulting with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians is essential for personalized recommendations and effective diabetes management.
Final Thoughts On Incorporating Orange Juice Into A Diabetic-friendly Diet
Incorporating orange juice into a diabetic diet can provide various benefits, such as vitamins and antioxidants. However, it is important to consider portion sizes, timing of consumption, and overall dietary balance. By following guidelines such as portion control and consulting with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians, individuals with diabetes can safely include orange juice as part of a balanced and diabetic-friendly diet. Remember to also prioritize a variety of fruits and vegetables, hydration, individualized meal planning, and regular physical activity to maintain overall health and manage blood sugar levels effectively.
FAQ: Is Orange Juice Good for Diabetics? Assessing Its Impact on Blood Sugar
Q1: Can diabetics drink orange juice?
Yes, diabetics can drink orange juice, but it’s important to consider its impact on blood sugar levels. Moderation and portion control are essential when consuming orange juice or any other food or beverage containing natural sugars.
Q2: How does orange juice affect blood sugar levels?
Orange juice contains natural sugars, mainly fructose, which can cause blood sugar levels to rise. This rise in blood sugar depends on various factors such as the amount consumed, the individual’s insulin sensitivity, and the presence of other foods or medications that may influence blood sugar.
Q3: Is orange juice a healthy choice for diabetics?
While orange juice contains essential nutrients like vitamin C and potassium, it is also high in carbohydrates and sugars. Therefore, it’s important to consume it in moderation and consider other options that provide the same nutrients without causing a rapid spike in blood sugar levels.
Q4: What is the recommended serving size of orange juice for diabetics?
The recommended serving size of orange juice for diabetics is typically around 4 ounces (120 mL). This allows for better portion control and reduces the impact on blood sugar levels compared to larger servings.
Q5: Should diabetics opt for freshly squeezed orange juice or packaged juice?
Freshly squeezed orange juice may contain fewer additives and preservatives compared to packaged juices. However, both types can impact blood sugar levels similarly due to their natural sugar content. It is essential to read labels carefully and consider factors like added sugars and portion sizes when choosing a product.
Q6: Are there alternatives to orange juice for diabetics?
Yes, there are several alternatives to orange juice that diabetics can consider. These include consuming whole oranges (which have more fiber), diluting juice with water, consuming low-sugar or sugar-free fruit juices, or choosing other beverages like infused water or herbal tea.
Q7: How can diabetics manage their blood sugar levels when drinking orange juice?
To manage blood sugar levels, diabetics can consider the following:
- Pairing orange juice with a source of protein or healthy fats to slow down the absorption of sugar.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels before and after consuming orange juice to gauge its impact.
- Adjusting medication or insulin doses if needed, in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Q8: What are the potential risks of consuming too much orange juice for diabetics?
Consuming excessive amounts of orange juice can lead to a rapid rise in blood sugar levels, which can be problematic for diabetics. It can also contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of dental cavities due to its sugar content.
Q9: Can diabetics drink orange juice in the morning?
Diabetics can drink orange juice in the morning, but it’s crucial to consider other factors such as their individual blood sugar levels, overall diet, and medication routine. It may be helpful to consult a healthcare professional to determine the best timing and portion size suitable for individual needs.
Q10: Is it better for diabetics to eat whole oranges instead of drinking orange juice?
Eating whole oranges is generally a better choice for diabetics as it provides more fiber and slows down the absorption of natural sugars. The fiber content in whole fruits aids in better blood sugar management and promotes satiety compared to consuming fruit juices.

Tropical Blendz Café and Juice Bar is a safe and clean environment where we provide immune-boosting natural juices, smoothies, shakes, authentic Caribbean cultural foods, and much more. Our juices are made from all-natural, unique fruits, vegetables, and herbs.